Making strides towards nutrition and gender equality in Nigeria
By Lilian Okafor, CS-SUNN
In Nigeria, malnutrition not only affects individuals, but also stunts economic growth and human development. The Women and Girls’ Nutrition Project is a collaborative effort implemented by the Civil Society-Scaling Up Nutrition in Nigeria (CS-SUNN), in partnership with FHI360, Alive & Thrive, 1,000 Days, and Intake, supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. The project aims to empower women and girls to achieve optimal nutrition and stand as crucial pillars for progress.
The project partnered with federal Ministries, Departments, and Agencies relevant to nutrition to develop a cross-cutting Action Agenda for women and girls’ nutrition in Nigeria that delivers healthy diets, care, gender equality, and a multi-system enabling environment as priorities for a thriving female from girlhood. These include:
- Support the nutrition department of the Federal Ministry of Women Affairs and Social Development to develop national guidelines on women and girls’ empowerment for optimal nutrition by September 2024.
- Secure commitments of Federal Ministries, Departments, and Agencies (MDAs) relevant to nutrition (Ministry of Health, Ministry of Women Affairs & Social Development, Ministry of Education, Ministry of Finance, Budget and National Planning, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) to increase the number of women in decision-making positions by at least 10% by 2024.
- Increase gender equity in the access and utilization of public economic empowerment schemes by at least 10% nationally by 2024.
- Increase awareness of professionals at the federal level, who have the potential to become champions, on the benefits of girls staying in school beyond basic education and the impact on nutrition outcomes.
Milestones Achieved:
The journey towards this transformative vision has been marked by a series of significant milestones:
- National Workshop on Women and Girls Nutrition: Leveraging momentum towards the pursuit of gender-inclusive nutrition, the National Workshop on Women and Girls Nutrition proved a pivotal event, uniting stakeholders from across Nigeria in a shared mission. Over two days, a dynamic blend of in-person and online participation brought together 167 virtual attendees with 30 enthusiastic on-site participants. Through a diverse array of activities spanning presentations, group discussions, and brainstorming sessions, participants collaborated to create an advocacy goal and four strategic objectives tailored to Nigeria’s unique context. Following this workshop, the coalition then agreed crafted a comprehensive advocacy strategy delineating actionable pathways towards achieving project objectives and engaging stakeholders across key sectors.
- National Guideline for Women and Girl’s Nutrition for Optimal Nutrition: CS-SUNN successfully achieved the primary objective of the Women Nutrition Project by supporting the Federal Ministry of Women Affairs and Social Development to develop a National Guideline on Women and Girls’ Empowerment for Optimal Nutrition. This involved convening a crucial gathering of nutrition stakeholders, including government ministries, agencies, and partners, to review and shape the guidelines content and framework. The resulting guideline, spanning six key sections, addresses critical aspects of empowerment principles, program initiatives, policies, coordination mechanisms, and implementation strategies. The Guidelines were recently validated and has been adopted by the key stakeholders including the Federal Ministry of Women Affairs, representing a key step towards empowering women and girls nationwide. It will be launched before the end of 2024.
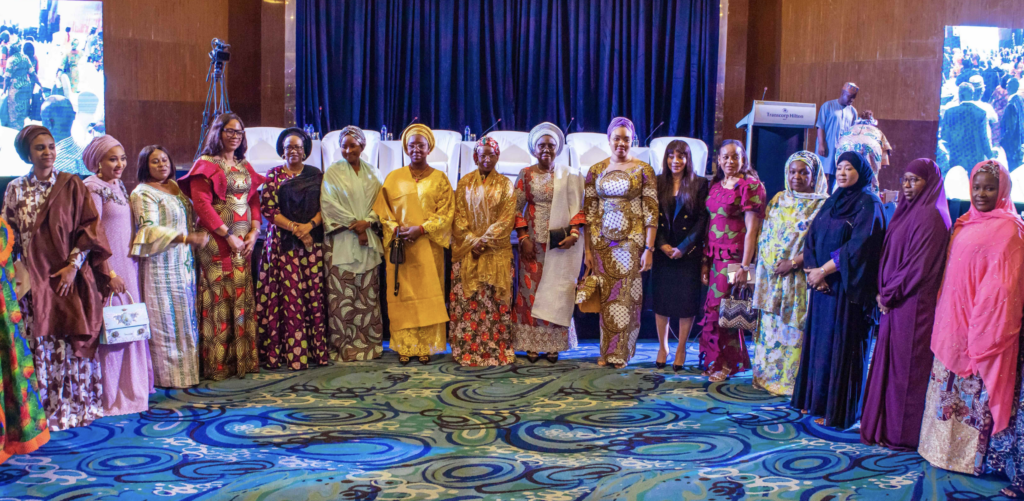
- Women In Power Conference: In May, the coalition hosted the Women in Power Conference for Nutrition, convening women from various spheres of society, including governor’s wives and accomplished professionals. The conference served as a platform to spotlight the pivotal roles women play in driving advancements in women and girls’ nutrition at the state level. Encouragingly, there is strong enthusiasm to establish this conference as an annual fixture in Nigeria, serving as a forum to evaluate the progress and commitments made by governor’s wives in advancing the nutrition agenda.

- Media Engagement: Leveraging the power of media, CS-SUNN organized media roundtable sessions to raise awareness, secure media support, and promote discussion on policy actions required on women and girls’ nutrition. The events garnered extensive coverage across prominent media, amplifying the discourse on this critical issue. With series of social media campaigns like; Women and Girl’s Nutrition: Why it Matters, gender equity in accessing public economic empowerment schemes, alongside the importance of girl-child education beyond basic schooling, CS-SUNN elevated awareness and advocacies for empowering women. Collaborating with partners such as Bridge Connect, wcyheIN, and Womenadvocate and leveraging visually appealing social cards and hashtags like #NutritionTuesday, #Nutri4Women, and #Nutri4Girls, trackable metrics underscored the campaigns’ impact, with significant reach and engagement rates observed across platforms.
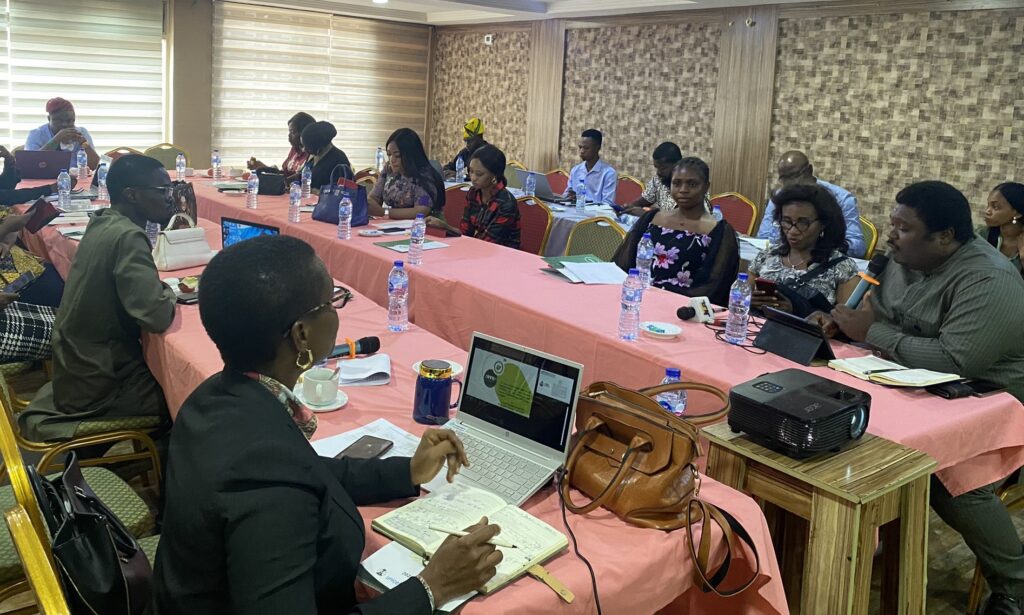

- Community Empowerment: Recognizing the importance of grassroots engagement, community town hall meetings were conducted to mobilize support from and empower local leaders. These interactions fostered commitments by community leaders to set up committees headed by cabinet members to sensitize households within their communities on the need to empower women and the girl child through access to quality education and livelihood support.
Looking Ahead
The Women and Girls’ Nutrition Project stands as a testament to the power of collaboration, innovation, and determination. Building on the momentum generated, the project will drive lasting change by: addressing cultural barriers through community involvement; educating mothers on the importance of girl-child education; introducing media study circles to deepen media coverage on women’s nutrition; and shifting an advocacy focus to implementation, ensuring that advocacy efforts translate into tangible policy changes and action.
Through concerted efforts and unwavering commitment, we move closer to a future where every woman and girl in Nigeria has the opportunity to thrive and to contribute to a healthier, more prosperous nation.